You may have heard of them but don’t know what they are, in this article we take a deep dive into answering the question “What are Amino Acids?”.
Amino Acids are known as the building blocks of life. There are currently around 500 known Amino acids identified which contribute to establishing life as we know it.
Amino Acids For Humans
For humans, there are between 22 needed to sustain life. However, they are not all important due to how they each are created.
Only 9 out of the 22 are essential as not every amino acid is made in the human body.
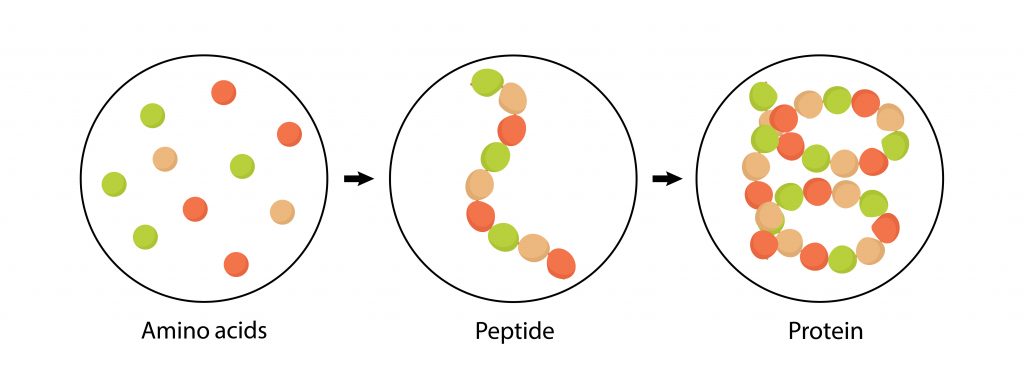
Once the amino acids are formed inside the human body, two or more bind together to create a chain known as a peptide. When a group of peptides form together, this creates a protein.
Once each amino acid is formed into a protein, the protein functions by using the amino acids as keys which unlock pathways which affect people physically, physiologically, and psychologically.
Amino Acids can appear in anything consumable such as fruits, grains, veggies, and meats.
Classifications of Amino Acids
There are three different classifications of Amino Acids with are called, which are Essential, Conditional and Non-Essential Amino acids.
Non-Essential Amino Acids are naturally occurring inside the human body; therefore, they don’t need any nutritional or lifestyle changes for a healthy person. The Non-Essential Amino Acids are:
⁃ Alanine, Aspartic Acid, Asparagine, Glutamic Acid, Serine, Selenocysteine and Pyrrolysine.
Conditional amino acids are very similar to non-essential amino acids, however, are beneficial in scenarios where the persons health condition is compromised by illness. This is when nutritional up-take is necessary for conditional amino acids to be made. The conditional amino Acids are:
– Arginine, Cysteine, Glutamine, Glycine, Proline and Tyrosine.
Essential Amino Acids are vital for human beings that can only be taken in through adequate nutrition from foods and fluids.
Essential Amino Acids are:
– Histine, Isoleucine, Leucine, Lysine, Methionine, Phenylalanine, Threonine, Tryptophan and Valine.
If someone is lacking essential amino acids, there are various side effects that can be experienced such as illness from a decreased immunity, digestive problems, depression, fertility issues in men and women, cognitive alertness issues and many more issues such as slow growth in children.
How are amino acids created and what do they do?
The following process below turns amino acids are turned into proteins by the work of RNA and DNA:
- DNA is located in the chromosomes and is held together by proteins called Histones.
- A multi-unit enzyme which can be imagined like 3 different blocks which known as an RNA Polymerase.
- The RNA Polymerase attaches to the DNA which is where the DNA helix is opened to attached individual DNA base which is made into a chain along the instructions of the DNA helix.
- Once the RNA is created, the RNA stand needs to mature into the codes that create a protein.
- The maturation means a unit made up of RNA and proteins come together to remove the portions of the non-coding RNA strands called the Introns whereas the coding portions are known as the Exons which is joined together by a complex of molecules known as a Spliceosome.
- Once the mRNA strand has the Introns removed, it leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm of the cell.
- Once the mRNA has left the nucleus, it attaches with a Ribosome which is the critical component to create proteins.
- Ribosome’s produces tRNA which reads the mRNA code and then delivers the relevant amino acids which creates chain inside the Ribosome that is separate from the mRNA.
- These chains may with finish amino acids in a chain to create a whole protein or finish with a partial chain which is known as a peptide.
- These chains eventually come together to create a protein.
Working
Each Amino Acid works differently with one another as they open the necessary receptors for where the nutrients are needed which depends on their specific purpose.
For example, if a cell passing through the brain that contains the amino acids Tryptophan, Tyrosine, Carnitine or Glutamine. These Amino Acids would only allow the appropriate vitamins or minerals to be released into the relevant area that benefits that particular part of the body.
If cells struggle to pass nutrients from the blood cells into a specific area, this would be due to a nutrient absorption condition that require special dietary, supplementary or medical intervention.
Another reason why nutrients may not get through to the correct area of the body. This could be due to reasons such as a viral or bacterial infection.
It depends on the disease; however, the body still works in similar ways on dealing with a new infection.
In this particular portion of this article, we won’t be addressing how amino acids affect bacterial infections but will only be referencing how the duty of amino acids are affected due to viral infections.
It depends on the type of virus infecting the host cell as some viruses have DNA however they are predominantly RNA based.
What is infection?
An infection of a foreign organism causes a protein spike as there needs to be sufficient amino acids to initiate the white blood cells to render the virus ineffective so the cells can reproduce without disruptions.
When there is a foreign virus in the body that has its own set of rules it operates by, an infection causes confusion in the how to interpret the DNA of the cell.
If this concept is hard to grasp, you can say that the proteins are like a bus driver working its designed duty to only then have an angry passenger start yelling and causing a scene. If the driver deems the angry passenger as a threat, then the driver may call on the white blood cells which are the police to settle the angry passenger, so they are no longer a threat.
Once the virus molecule become redundant, the amino acids beings to regulate their function within the cells.
Foreign infections within the human body arise frequently, however they are not always symptomatic.
In order to prevent symptomatic infections, it is important to maintain a well-balanced diet which allows for sufficient uptake in amino acids, so threats are addressed appropriately.
Essential Amino Acids
Out of the 22 Amino Acids, 9 need to be replenished to functionally keep the human body at its healthiest.
Amino acid deficiency can be felt in numerous ways such as dizziness, lathergy, depression, mal-absorption, muscular pain and many more symptoms such as a prolonged recovery from exercise.
Consuming too much amino acids can lead symptoms such as nausea, loss of coordination, stomach cramps, headaches, fatigue, issues with mood and sleep.
Consuming protein within a 30-minute time frame is known as the anabolic window.
The window refers to the belief that after a workout the best time for protein is within the first 30 minutes. There may be some truths to that belief however evidence from multiple studies that the anabolic window might be open far longer than the believed 30 minutes.
Another study suggests consuming protein before a workout may be more beneficial than after the workout as the amino acids are synthesising during the workout.
Protein Options

People always have their dietary preferences for various reasons which influences the type of protein consumed.
Animal proteins contain all the necessary amino acids which is why it is recommended to consume animal proteins however for a complete and healthy diet, the recommendation is to have both plant and animal proteins respectively. Plant proteins can have a complete essential amino acid profile, however, there needs to be a strategy when consuming plant proteins as not all plants have all of the amino acids.
There are some great options of plants with a complete essential amino acid profile such as: Quinoa, Soy, Buckwheat, Hemp, Chia Seeds, Spirulina, Tempeh and Amaranth.
The breakdown of the amino acids is slower in plant proteins than amino acids from animals, but that doesn’t mean you don’t get any benefits from animal proteins.
This is why advice exists to maintain a high protein diet regardless of the training regime.
For those that don’t want the extra nutrition from foods which may complicate achieving the ideal training results. There are plenty of supplement options out in the market for optimal recovery.
There’s many versions of protein products which may or may not contain nutrients such as fats and carbohydrates but will be very beneficial. In an earlier article about electrolytes, we mention the benefits of sugar in some formulas. (Have a read here if you missed out on reading the article.)
Forms of Protein
Casein:
This is a type of protein that is slower at absorption which is why it’s ideal for consumption for use during the night. Casein is one of the most nutritious and purest proteins, however not everyone can tolerate this form due to many reasons such as lactose intolerance.
Mass Gainer:
This is the ideal protein for those who wish to get bigger muscles. Mass gainers contain more carbohydrates over general Whey Protein Concentrate as carbohydrates act as a vital food source that allows muscles to grow.Important to note, mass gainers don’t magically make your muscles grow unless you have the correct training routine.
WPC – Whey Protein Concentrate:
This is one of the fastest acting proteins that can be consumed before or after a workout as a snack or meal replacement. With how Whey Protein Concentrate is developed, there are many other health benefits that can be derived from whey protein due to the nutrient rich properties.
WPI – Whey Protein Isolate:
This is the protein that is ideal for consuming after a workout or strenuous activity. This version contains very little lactose, carbohydrates and fats which allows for fast absorption of the amino acids into the blood stream.
Hydrolysed Proteins:
Hydrolysed protein can originate from any source such as plant proteins and whey. The cost of creating hydrolysed proteins is significantly more than creating other proteins.
The key differences between hydrolysed proteins and others are that hydrolysed protein powder is finer than other proteins like WPC and the amino acid molecules are finer, so absorption is far greater and quicker.
Plant Proteins:
There are very few plants that provide all the Essential Amino Acids for humans. However, it doesn’t mean they aren’t easy to find. There are many vegan protein products coming to market with complete essential amino acids.
- Soy is a great protein because it is one of the few plants that contains all the amino acids for humans. If consuming vegan proteins is ideal, it is important to check that the protein generally has 2+ types of plant proteins involved. A good pair of plant proteins can ensure there is enough amino acids is found in Rice and Pea proteins.
- There are other formulations of plant proteins may have more than two forms of proteins as the different sources of proteins can provide other benefits such as improved taste and health benefits.
Branch Chain Amino Acids
During and after a workout or in the middle of a strenuous day where it can be physically taxing. Amino Acids can still be consumed to make recovery better.
Branch Chain Amino Acids which are also known as BCAA’s are commonly known to benefit people who suffer from fatigue by assisting with the prevention of the breakdown of muscular tissue.
The three BCAAs are Leucine, Isoleucine and Valine. These are the best identified as the most important Amino Acids which are key to stopping the breakdown of soft tissues.
The role each amino acid plays in the BCAA formula are below:
- Leucine has been identified through multiple studies to be the best amino acid that initiates protein synthesis. The role of this amino acid is to initiate protein synthesis by activating the mRNA to begin reading the DNA and formulating proteins. The other essential role for Leucine is to release insulin into the blood stream which benefits muscle growth by encouraging glucose absorption.
- Isoleucine acts very similar to the function of Leucine; however, Leucine doesn’t regulate blood sugar levels as its primary role is to initiate the synthesis of proteins. Isoleucine has an additional function which is to regulate the levels of insulin.
- Valine is critical component maintaining and encouraging nutrient uptake such as glucose and other nutrients such as vitamins and minerals which position the muscle to grow.
More about BCAA
BCAAs make up 40% of a protein organism. Hence, three are the most critical for recovery and basic function.
BCAA’s come from plant and animal proteins. The formulation of this product allows you for consume it even during the most strenuous workouts. Unlike whey and vegan proteins which may cause discomfort.
There are other products with BCAAs that also contain EAAs. This is a great combination for that who have more specific training goals where EAAs don’t have to be consumed through food but can be consumed through supplements.
Leucine
Leucine has been shown to only work if there is sufficient glucose in the system which allows for the muscles to begin recovery.
Glucose is made from foods and therefore if you want to fast but built muscle, it is important to understand how fasting and not fasting can benefit your training goals.
According to many studies, there needs to be sufficient Leucine in the body for muscles to sufficiently grow. When choosing an ideal BCAA, there hasn’t been much evidence to give credible evidence to the theory that protein synthesis is better above a ratio of 3 parts Leucine to 1 part Isoleucine and 1 part Valine.
Any more than 3 parts Leucine may trigger symptoms relating to intolerance. However, the concept of including more Leucine in the BCAAs starts with the idea. This is manifested from multiple studies that proved Leucine initiates the uptake of glucose.
Theres no indication that a 10:1:1 ratio of Leucine to Isoleucine/Valine is any better at initiating better muscle growth. What is better for muscle growth? Ensuring adequate carbohydrates and sugars within an appropriate time frame as these compounds are vital for developing muscle and size.